Choosing the Right Server Size - Instance Types
Lesson 6
When you go car shopping, you choose between different models - a compact car, an SUV, or a truck - based on what you need. Cloud servers work the same way! AWS offers different “sizes” and “types” of servers for different purposes.
Think of instance types like choosing a vehicle:
- Compact car = Small, cheap, good for daily commuting (basic websites)
- SUV = Bigger, more powerful, good for families (business applications)
- Pickup truck = Specialized for heavy work (data processing)
- Sports car = High performance for specific needs (gaming, graphics)
Your job: Match the right server type to what your project needs. Don’t worry - you’re not expected to memorize all the options! You just need to learn how to pick the right one.
Understanding Server Components (The Basics)
Before we choose server types, let’s quickly understand what makes servers different from each other:
CPU (vCPUs) - The Brain
What it is: The “brain” that does all the thinking and calculations
Like: A chef in a kitchen - more chefs = more meals prepared at once
AWS calls them: vCPUs (virtual CPUs)
More = better for: Complex calculations, running multiple programs
Memory (RAM) - Short-term Storage
What it is: Where the server keeps information it’s currently working on
Like: Your desk space - bigger desk = more papers you can work on at once
AWS measures in: GiB (like gigabytes, but slightly different)
More = better for: Handling lots of users, keeping data readily available
Performance Types
Burstable: Like a car with turbo - normally runs steady, but can “burst” to high speed when needed
Steady: Like a reliable truck - consistent performance all the time
Optimized: Like a race car - built for one specific thing (speed, cargo, etc.)
Don’t worry about memorizing this! We’ll explain terms as we go. Let’s see how this works with real examples.
Table of contents
- Choosing the Right Server Size - Instance Types
- Example 1: A Business Website
- Example 2: A Video Game Studio
- Example 3: A Data Analysis Company
- What You’ve Accomplished
Example 1: A Business Website
The scenario: A local restaurant wants to put their website online. They expect normal traffic most of the time, but sometimes they get busy (like during lunch rush or after posting on social media).
What they need:
- Type: General purpose (like an SUV - good for most things)
- Performance: Burstable (like turbo - steady most of the time, fast when busy)
- Brain power: 4 vCPUs (4 “chefs” working)
- Memory: 16 GiB (big enough “desk” for their work)
- Budget: As cheap as possible while meeting their needs
Step 1: Find the right category
Visit AWS instance types and you’ll see categories like a car dealership:
- General Purpose = Good all-around vehicles (SUVs, sedans)
- Compute Optimized = Sports cars (fast processors)
- Memory Optimized = Moving trucks (lots of storage space)
Since our restaurant wants an all-around server, we pick General Purpose.
Step 2: Find burstable performance
In General Purpose, you’ll see tabs like T3, T4g, A1 - these are like different car models. We need one that says “burstable” (the turbo feature).
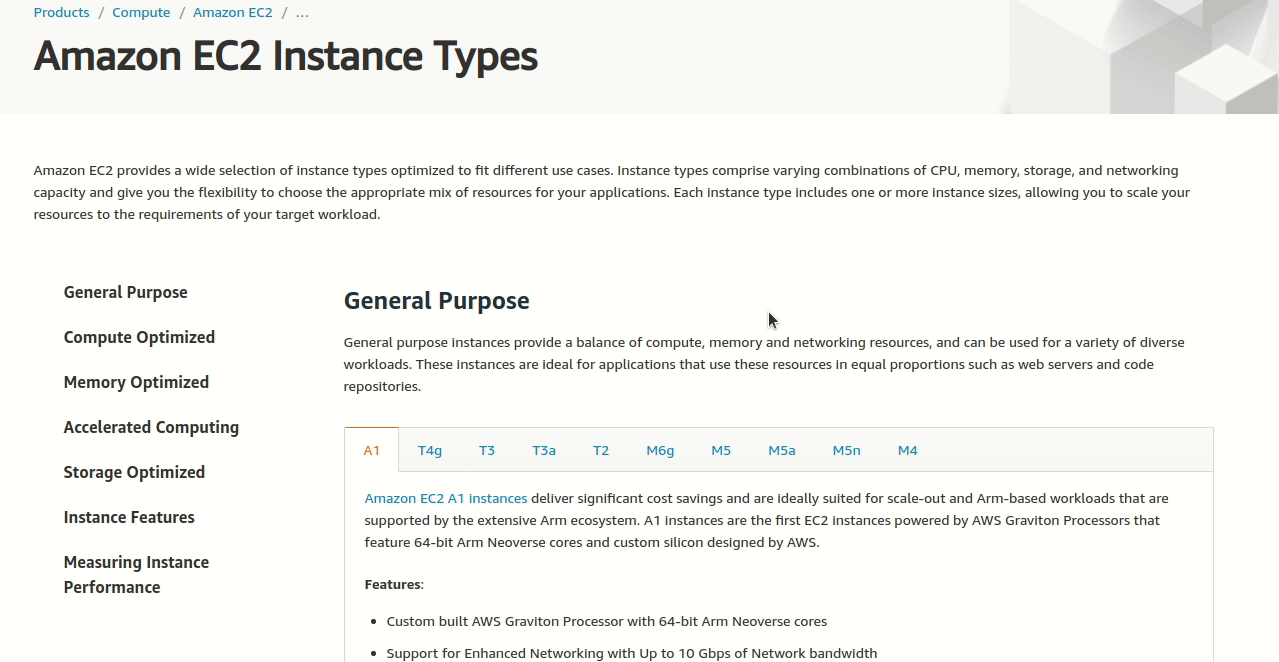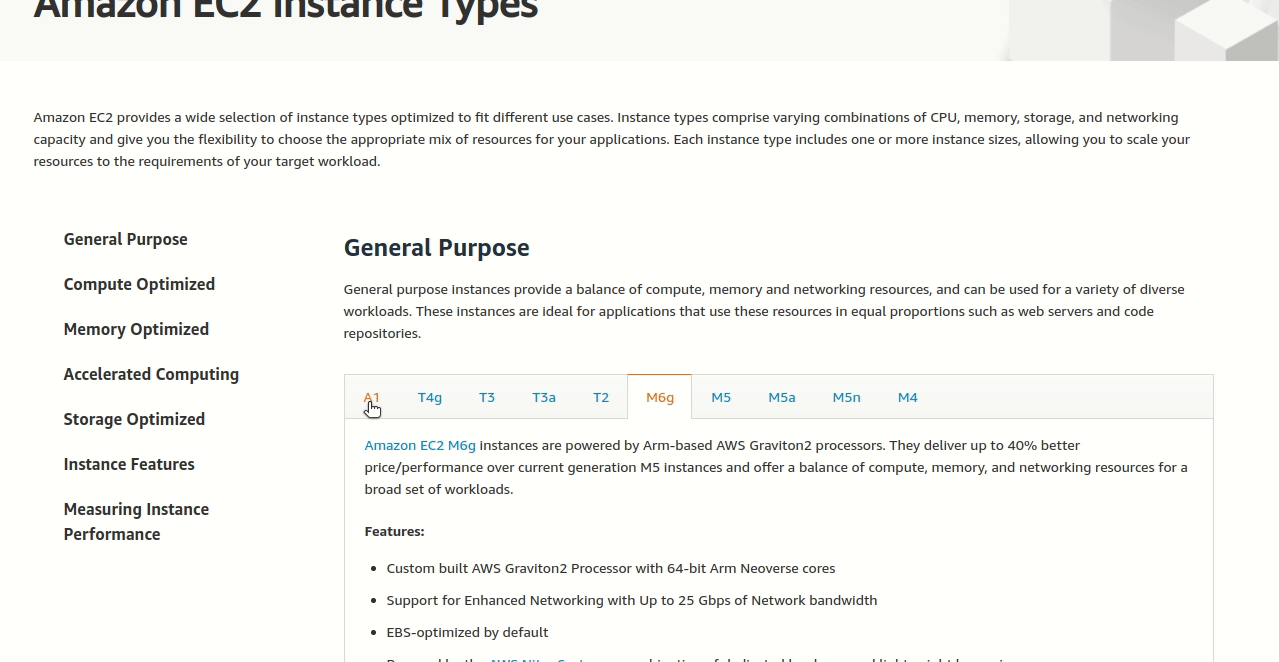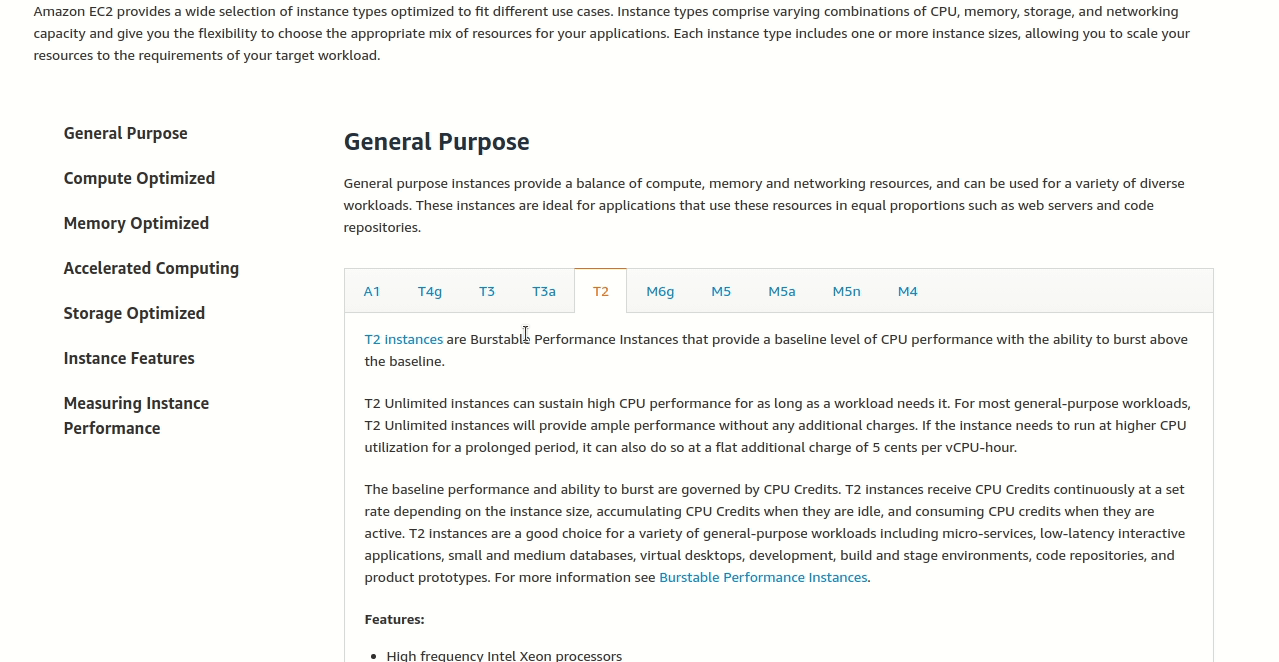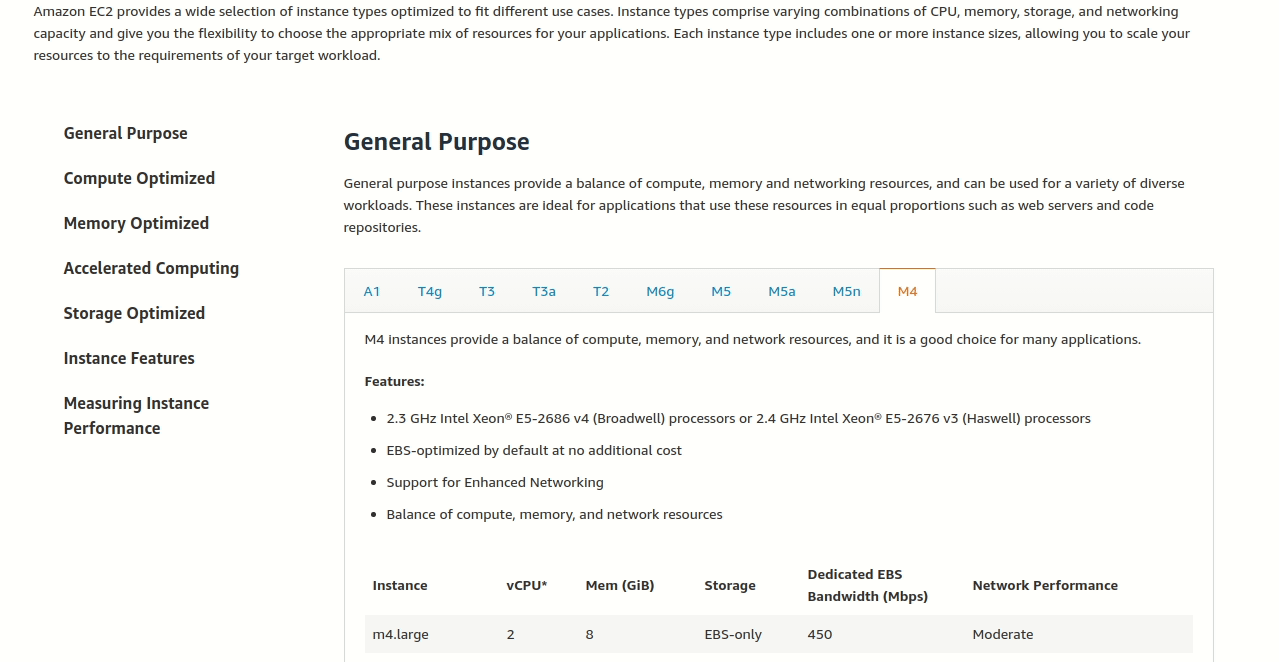
Step 3: Pick the best family for websites
You’ll find three “burstable” families: T3, T3a, and T2. Think of these like different car brands - all make SUVs, but some are better for certain things.
Look for the “Use Cases” section (like reading what each car is good for). For websites and web applications, T2 is specifically mentioned as ideal.

Step 4: Find the right size
Now we need a T2 instance with enough power for our restaurant:
- At least 4 vCPUs (4 chefs in the kitchen)
- At least 16 GiB memory (big enough desk space)
Looking at the T2 table, we can see the options like t2.small, t2.medium, t2.large, etc. Find the smallest one that meets our minimums:
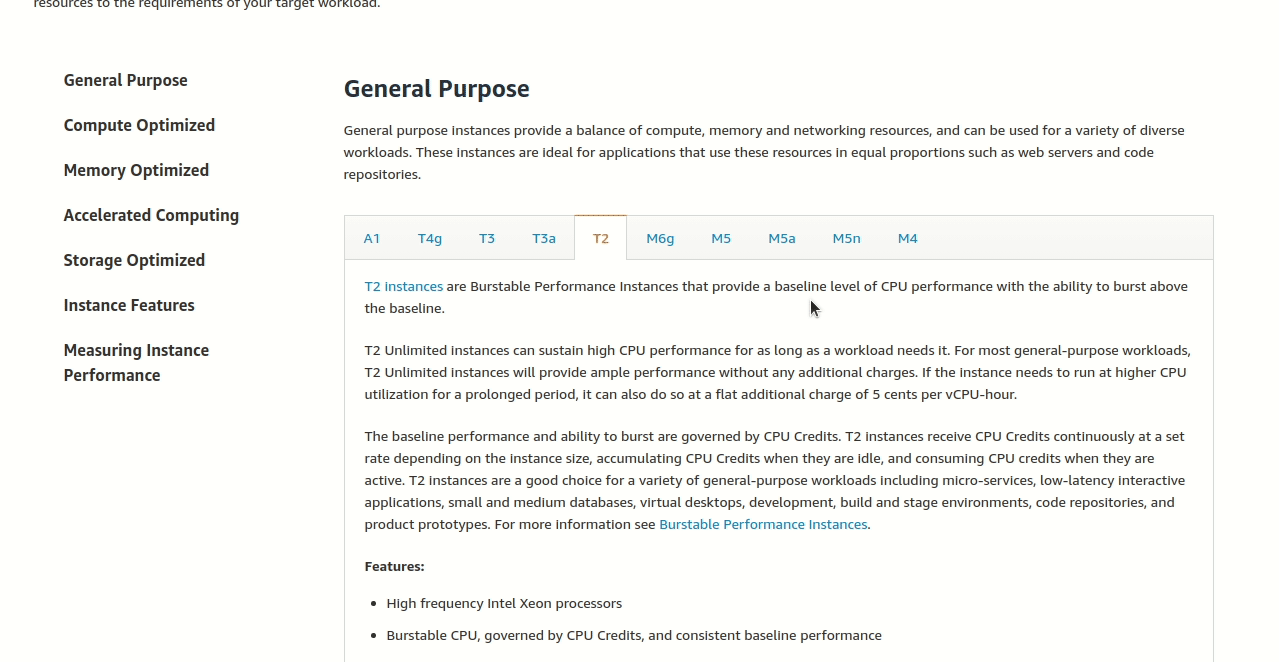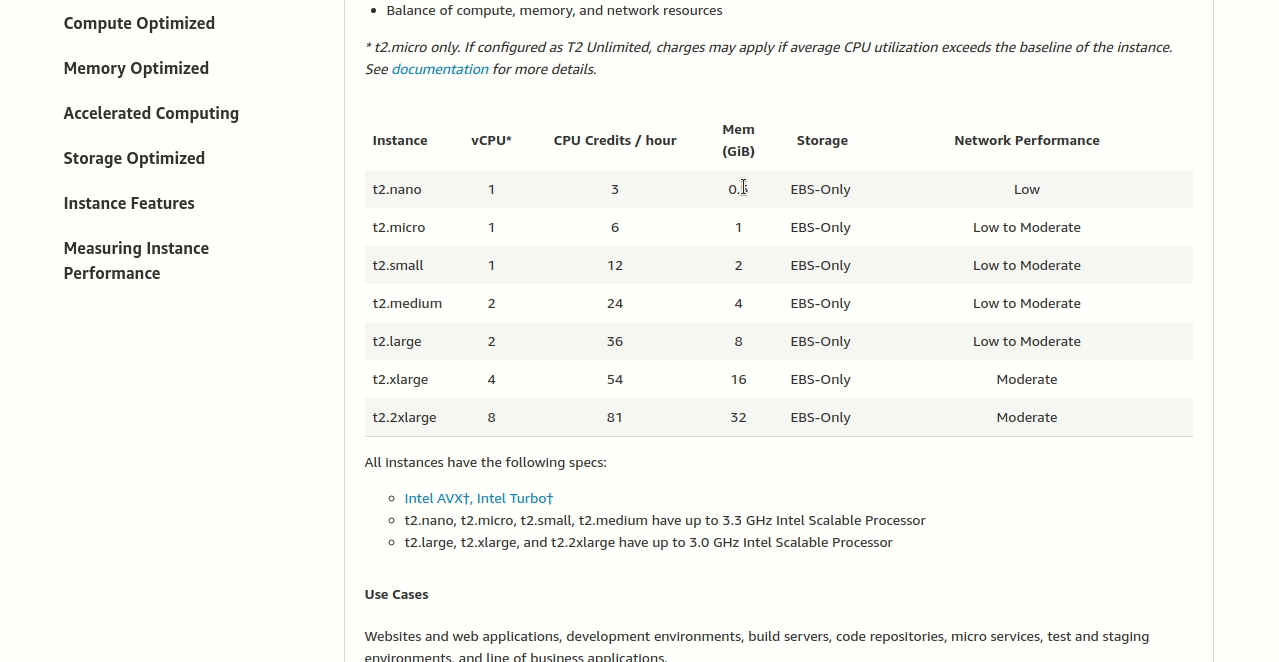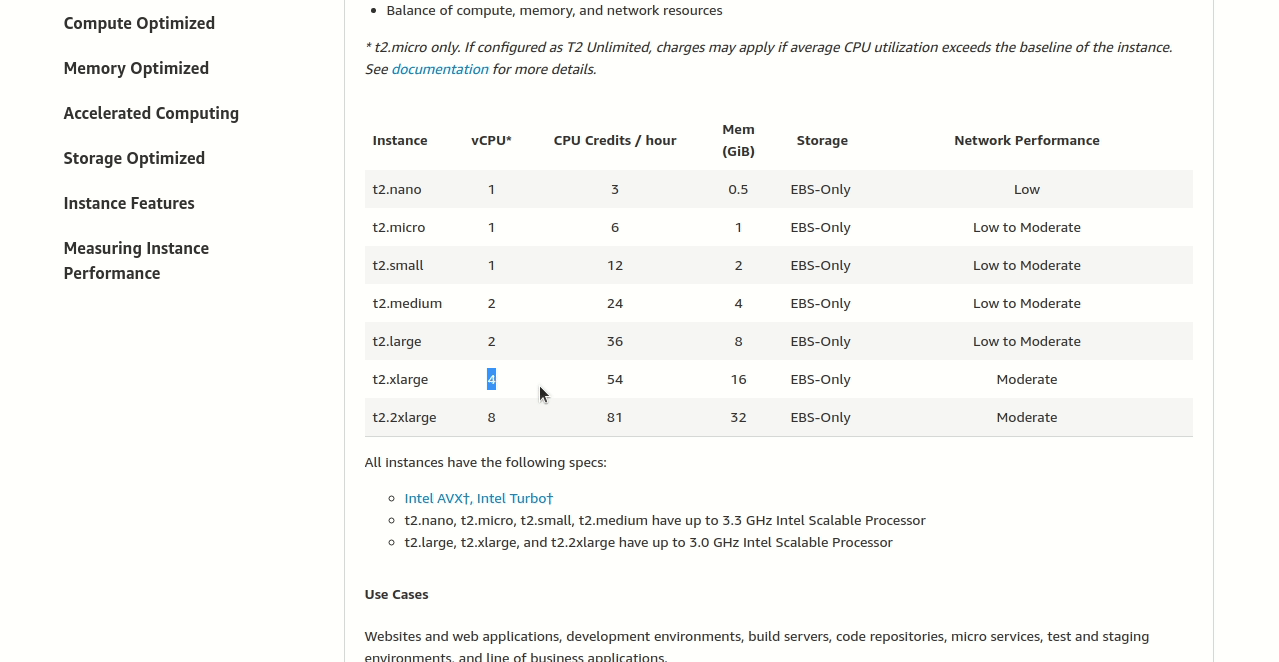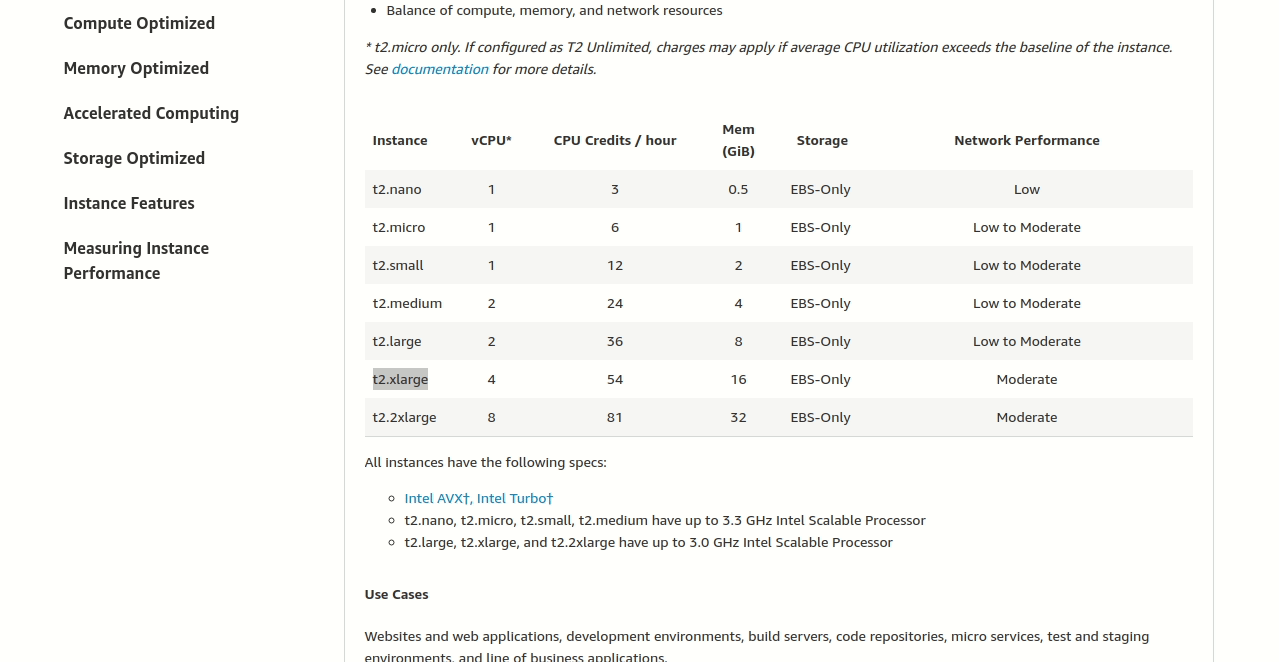
The answer: t2.xlarge
This gives us exactly 4 vCPUs and 16 GiB memory - perfect for our restaurant’s website! It’s the cheapest option that meets their needs.
What we learned:
- General Purpose → Good for typical websites
- Burstable → Handles traffic spikes (lunch rush!)
- T2 family → Best for web applications
- t2.xlarge → Smallest size meeting their requirements
Example 2: A Video Game Studio
The scenario: A small video game studio creates 3D games and animations. They need a server that’s like a high-end gaming computer - specialized for graphics and visual processing.
What they need:
- Type: Specialized for graphics (like a race car built for speed)
- Special feature: Hardware accelerators (like turbo chargers for graphics)
- Purpose: 3D graphics, game development, visual effects
- Brain power: 16 vCPUs (16 “artists” working on graphics)
- Memory: Only 4 GiB (they don’t need much “desk space”)
Key terms to understand:
- Graphics processing = Creating images, videos, 3D models (like drawing, but by computer)
- Hardware accelerators = Special chips that make graphics super fast (like having a professional artist vs. a regular person drawing)
- 3D visualizations = Making 3D models and animations (like Pixar movies)
Your turn to try!
Before reading the solution, try to find the right instance type using AWS’ instance types. Look for keywords like “graphics”, “accelerated”, or “3D”.
Hint
This won’t be “General Purpose” - games need specialized hardware, like how race cars aren’t regular cars!
Solution:
Step 1: Find the right category
This isn’t a general purpose server - it’s specialized! Look for “Accelerated Computing” which is like the “sports car” section of AWS servers.
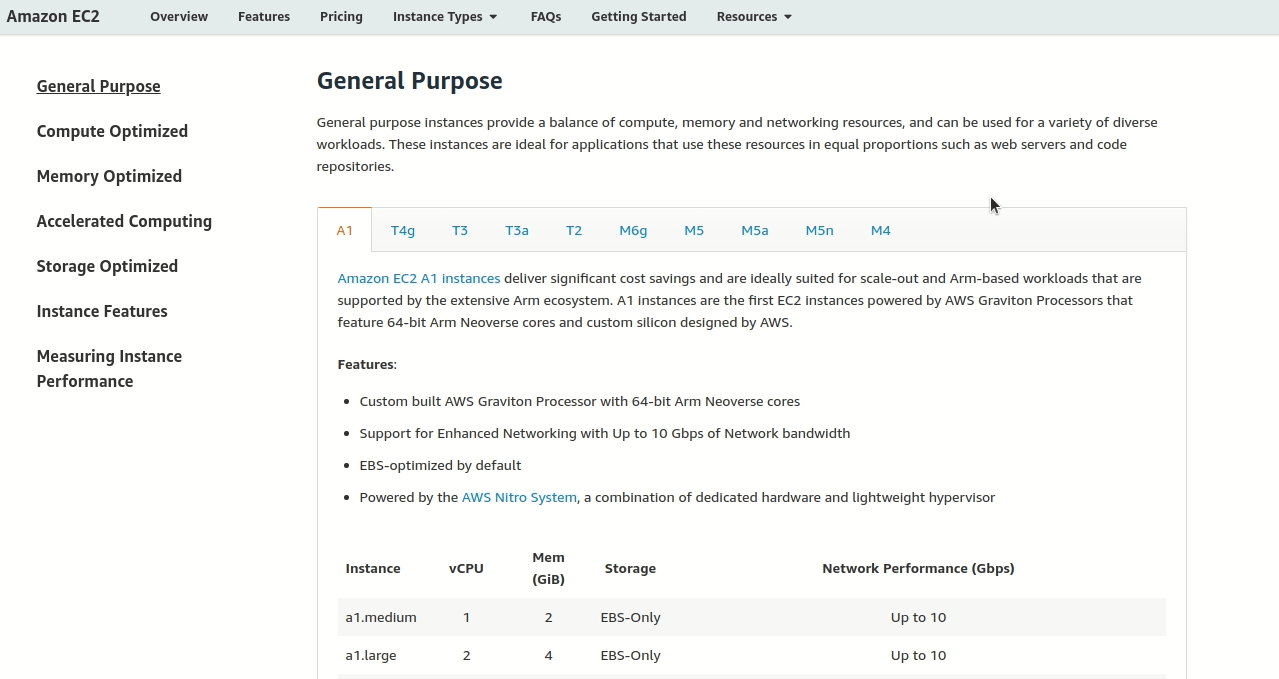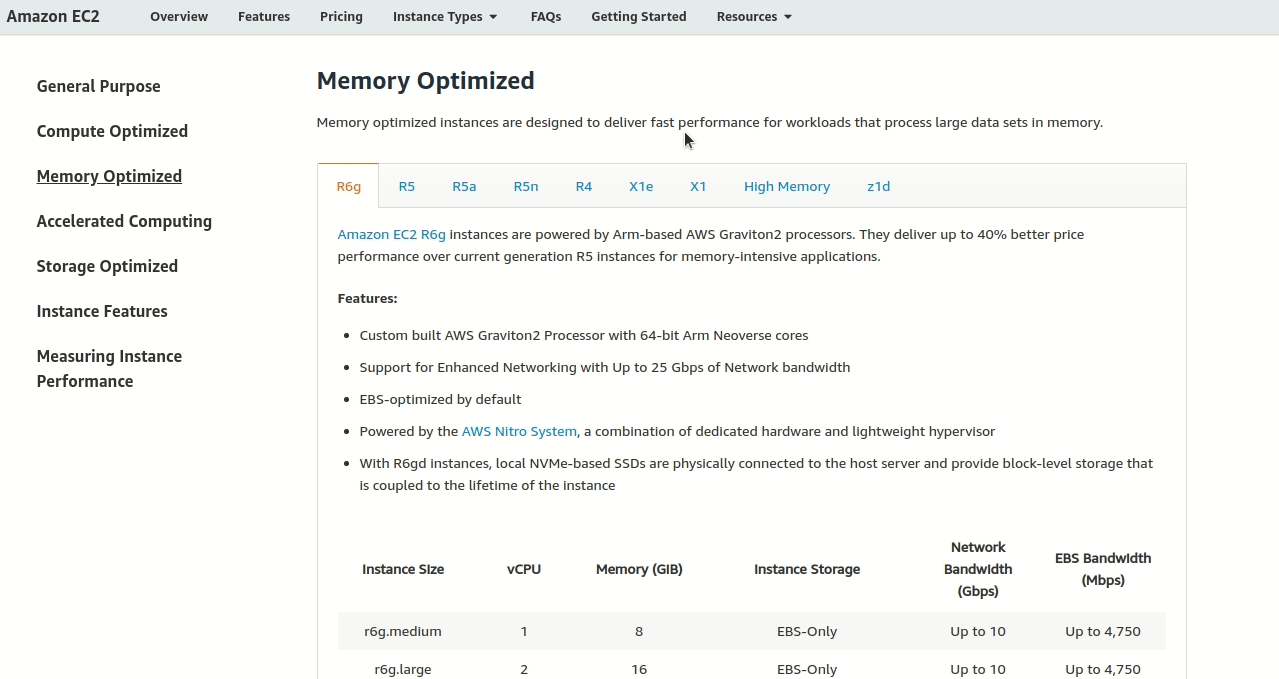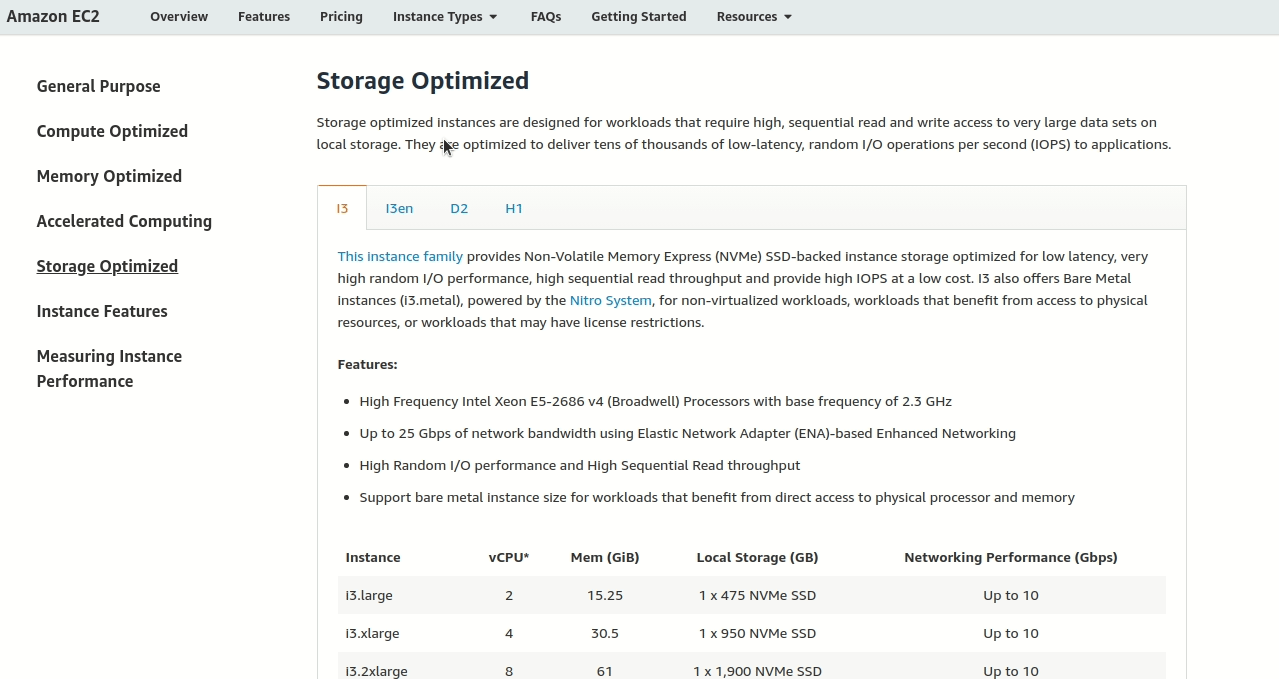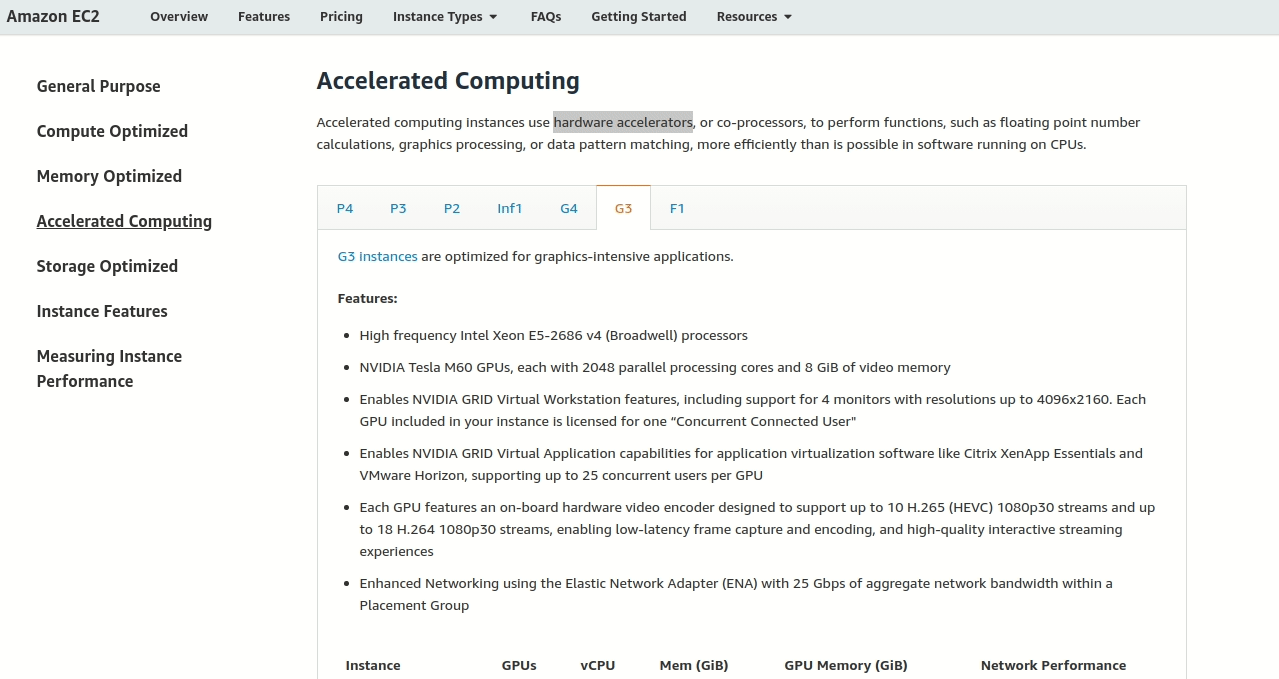
Step 2: Find graphics-specialized servers
In Accelerated Computing, look at the “Use Cases” sections. You’ll find that G4 and G3 families are built for graphics work (like gaming PCs vs. regular computers).
Step 3: Pick the best for 3D work
Read the descriptions carefully:
- G4: Good for graphics in general
- G3: Specifically mentions “3D graphics” (perfect for our game studio!)
Step 4: Find the right size
Our game studio needs:
- At least 16 vCPUs (16 “artists”)
- At least 4 GiB memory (small “desk” is fine)
Looking at the G3 table, the g3.4xlarge gives us exactly 16 vCPUs and 122 GiB memory - way more memory than needed, but it’s the smallest option that has enough vCPUs.
What we learned:
- Specialized needs → Accelerated Computing category
- Graphics work → G3 family (built for 3D)
- g3.4xlarge → Smallest option meeting requirements
Note: There are larger, more powerful options, but following the “cheapest that works” rule saves money!
Example 3: A Data Analysis Company
The scenario: A company analyzes huge amounts of data in real-time (like tracking millions of website visits as they happen). They need a server with a massive “desk” to spread out all their work.
What they need:
- Type: Memory optimized (like a moving truck - lots of storage space)
- Purpose: Big data analytics, real-time processing
- Brain power: 32 vCPUs (32 “accountants” crunching numbers)
- Memory: 256 GiB (enormous “desk” to hold all the data)
- Budget: Cheapest option that meets their needs
Key terms to understand:
- Big data analytics = Analyzing huge amounts of information (like counting every grain of sand on a beach)
- Real-time = Processing information instantly as it comes in (like live sports commentary)
- Memory optimized = Built to hold lots of information at once (like a library vs. a small bookshelf)
Your challenge:
Try to find the right instance type yourself! Look for servers that are good with lots of memory and data processing.
Hint
Think “moving truck” not “sports car” - they need space, not speed!
Solution
Step 1: Find the right category
Since they need lots of memory (256 GiB!), look for Memory Optimized - the “moving truck” section of AWS.
Step 2: Find real-time data processing
Look through the Memory Optimized families (R5, R6g, X1e, etc.). Only the R families mention “real-time data processing” in their descriptions.
Step 3: Pick the most cost-effective generation
You’ll see different generations like R5, R6g, etc. (like model years for cars):
- R6g: Newer generation, better price/performance (40% better than R5!)
- R5: Older generation, more expensive for same power
For budget-conscious clients, choose the newer R6g.
Step 4: Find the right size
Look at the R6g table and find the smallest instance with:
- At least 32 vCPUs (32 “accountants”)
- At least 256 GiB memory (big enough “desk”)
Answer: r6g.8xlarge
This gives exactly 32 vCPUs and 256 GiB memory - perfect fit at the lowest cost!
What we learned:
- Lots of memory needed → Memory Optimized category
- Real-time processing → R family
- Budget conscious → Newer generation (R6g)
- r6g.8xlarge → Exact fit for requirements
What You’ve Accomplished
✅ Learned the basics of server components - CPU, memory, and performance types
✅ Understood the car analogy - Different server types for different needs
✅ Practiced real-world scenarios - Restaurant website, game studio, data company
✅ Learned the decision process - Category → Family → Size
✅ Experienced budget considerations - Finding the cheapest option that works
You now think like a cloud architect! You can match technical requirements to the right server types.
The Big Picture
What you learned applies everywhere:
- Requirements gathering: Understanding what clients actually need
- Product research: Navigating technical specifications to find solutions
- Cost optimization: Getting the best value for specific needs
- Decision frameworks: Step-by-step approaches to complex choices
Important Reminders
🎯 You DON’T need to memorize instance types! Even experienced professionals look them up.
🎯 You DO need to understand the process: Category → Family → Size based on requirements.
🎯 Practice makes perfect: The more you work with these, the more intuitive it becomes.
Interactive Practice - Test Your Skills!
Now it’s your turn! Try these real-world scenarios. Type your answer in the box and click “Check Answer” for instant feedback.
Scenario 1: Small Business Blog
The situation: A local bakery wants a simple blog to share recipes and store hours. They expect light traffic most of the time, but occasionally get busy when they post new recipes on social media.
Requirements:
- Budget: Very tight, want cheapest option
- Performance: Burstable (handle occasional traffic spikes)
- Power needed: Minimal - just a simple blog
- Use case: Web hosting
Your answer: What instance type would you recommend?
Scenario 2: Machine Learning Startup
The situation: A tech startup is training AI models to recognize images. They need serious computational power to process thousands of images quickly.
Requirements:
- Type: Compute-intensive work
- Performance: High CPU power for calculations
- Power needed: 16+ vCPUs for parallel processing
- Use case: Machine learning, artificial intelligence
Your answer: What instance type would you recommend?
Scenario 3: Architectural Firm
The situation: An architecture firm needs to run 3D modeling software and render building designs. They create detailed 3D visualizations for client presentations.
Requirements:
- Type: Graphics-intensive work
- Performance: GPU acceleration for 3D rendering
- Power needed: 8+ vCPUs, specialized graphics hardware
- Use case: 3D visualization, architectural rendering
Your answer: What instance type would you recommend?
Scenario 4: Financial Trading Platform
The situation: A financial company processes millions of stock trades in real-time. They need to keep massive amounts of current market data in memory for instant access.
Requirements:
- Type: Memory-intensive work
- Performance: Real-time data processing
- Power needed: 64+ vCPUs, 500+ GiB memory
- Use case: High-frequency trading, real-time analytics
Your answer: What instance type would you recommend?
Scenario 5: E-commerce Store
The situation: An online store sells handmade crafts. They get steady traffic during the day but big spikes during sales events and holidays.
Requirements:
- Type: General purpose web application
- Performance: Burstable to handle sale events
- Power needed: 4 vCPUs, 8 GiB memory
- Use case: E-commerce website, web applications
Your answer: What instance type would you recommend?
Next Steps
Ready to explore more AWS features? Head to Everything Else EC2 where you’ll discover additional tools and capabilities!
Pro Tip: Bookmark the AWS Instance Types page - you’ll be using it throughout your career!